
Our mission is to ensure the generation of accurate and precise findings.
Contact Us Avalonnaturals, 4-92 , Auriga Drive, Ottawa, ONK2E 8Z8, Canada info@avalon-naturals.comAveoxx Advance The only Natural product meant for all types of Arthritic& Rheumatic Disorders.
Aveoxx Advance is solution for all types of Arthritic& Rheumatic Disorders.
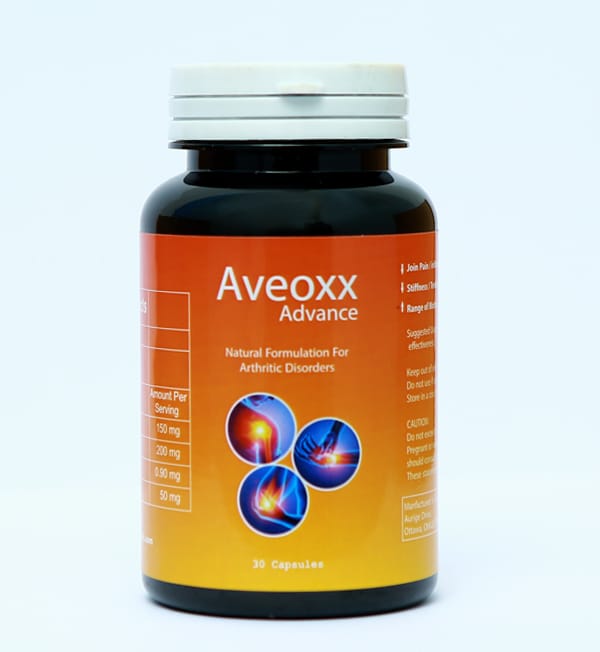


The only Natural product meant for all types of Arthritic& Rheumatic Disorders
Take 1-2 capsule per day with or without a meal.
30 Caps
Generally None

All types of Arthritic & Rheumatic Disorders
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Gout

Suguru Ito, Akihiro Ohmi, Akiyo Sakamiya, Takeo Yano, Katsuzumi Okumura,
Norihiro Nishimura & Kazuhiro Kagontani
To cite this article: Suguru Ito, Akihiro Ohmi, Akiyo Sakamiya, Takeo Yano, Katsuzumi Okumura,
Norihiro Nishimura & Kazuhiro Kagontani (2016) Ginger hexane extract suppresses RANKLinduced
osteoclast differentiation, Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 80:4, 779-785,
DOI: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1127133
To link to this article: https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2015.1127133
Effectiveness of Boswellia and Boswellia extract for osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ganpeng Yu, Wang Xiang, Tianqing Zhang, LiutingZeng, Kailin Yang & Jun Li
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies volume 20, Article number: 225 (2020)
Therapeutic role of dual inhibitors of 5-LOX and COX,selectiveand non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
J Martel-Pelletier, D Lajeunesse, P Reboul, J-P Pelletier
Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:501–509
Man-Kyo Chung 1,* and James N. Campbell 2,*
1 Department of Neural and Pain Sciences, University of Maryland, School of Dentistry,
Program in Neuroscience, Center to Advance Chronic Pain Research, Baltimore, MD 21201, USA
2 Centrexion Therapeutics, Baltimore, MD 21202, USA
* Correspondence: mchung@umaryland.edu (M.-K.C.); jcampbel@jhmi.edu (J.N.C.);
Tel.: +1-410-706-4452 (M.-K.C.); +1-410-369-2201(J.N.C.)
Academic Editors: Arpad Szallasi and Susan M. Huang
Received: 7 September 2016; Accepted: 27 October 2016; Published: 1 November 2016
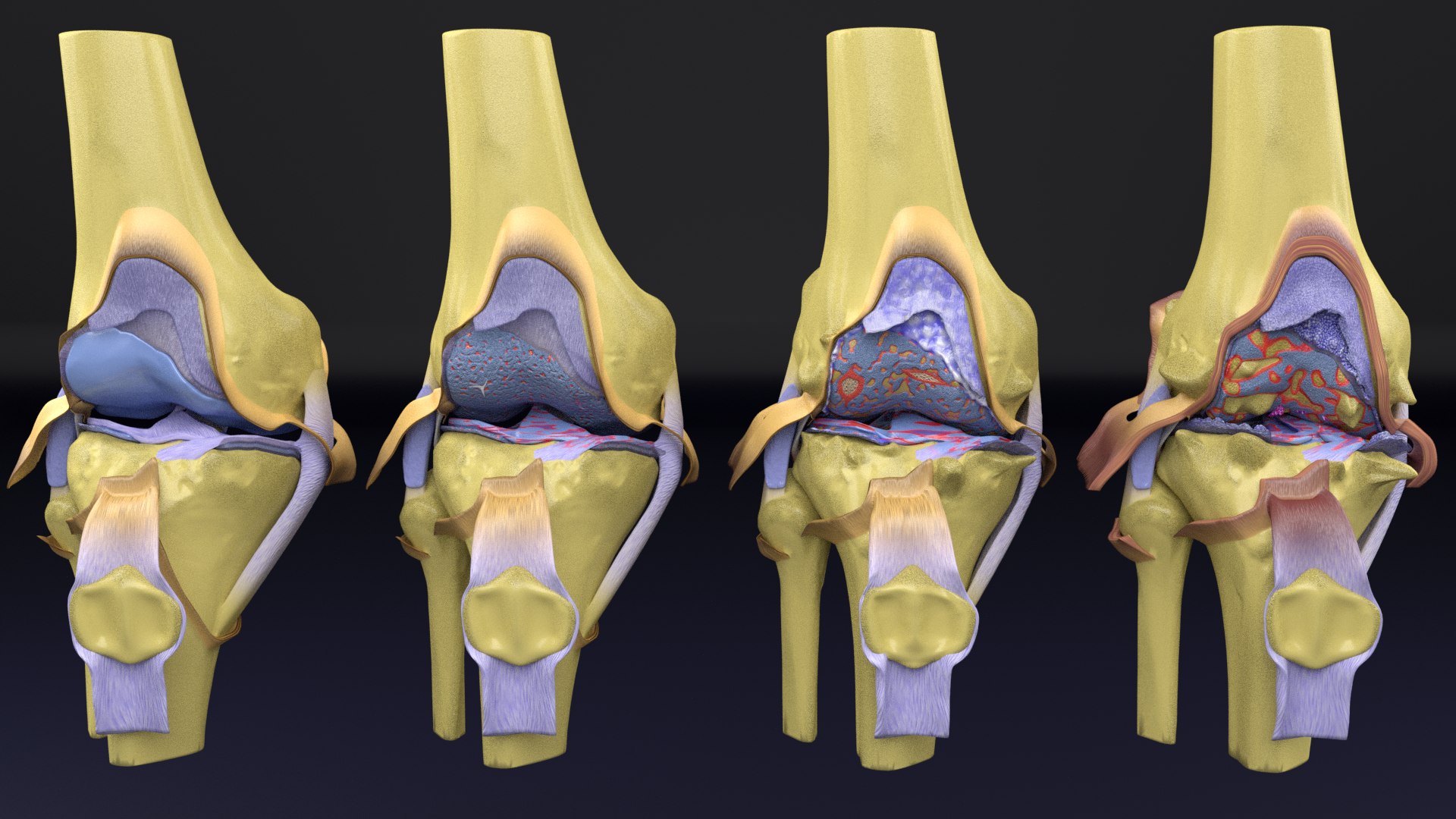 What are the 4 Stages of Osteoarthritis?
What are the 4 Stages of Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a common disorder, occurring at any age. Each stage of osteoarthritis affects the joint in different ways. According to studies, the 4 distinct stages of osteoarthritis includes,
 Stage 1: Early Osteoarthritis
Stage 1: Early Osteoarthritis
Early osteoarthritis is the first stage of joint degradation. In early osteoarthritis, the cartilage layer of the joints starts to break down causing stiffness, and pain. This stage causes minor deformity in bone structure. However, physical activity is not affected.
SymptomsEarly osteoarthritis can show various symptoms which may include:
Early osteoarthritis causes minor changes in the affected joints including:

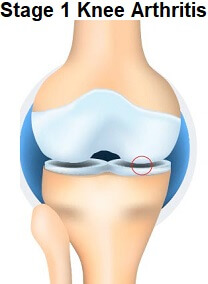
If you have been diagnosed with Ist stage of osteoarthritis, following prevention strategies may be opted to slow down the symptoms:
Moderate osteoarthritis is the second stage of osteoarthritis. It is a progression of the early stage of osteoarthritis where symptoms are mildly aggravated. The initiation of pain and swelling interfere with overall physical activity of a person.
SymptomsSome of the commonly noticed symptoms of moderate osteoarthritis include: Significant decrease in joint motion
If you have moderate osteoarthritis, you may experience changes in the joints which include:

During moderate osteoarthritis, the disease has progressed to a limit. However, you can still manage the symptoms using prevention strategies like:
Severe osteoarthritis is the third stage of osteoarthritis. It is characterized by chronic inflammation in the affected joints, which further leads to excessive pain and tenderness in the joints. It affects the physical activity to a great extent.
SymptomsThe third stage of osteoarthritis gives rise to symptoms which may include:

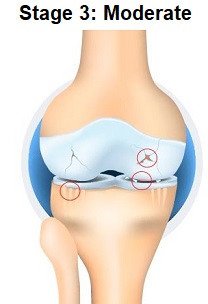
Severe osteoarthritis causes excessive damage to the joints. A proper management plan to deal with this stage is hence necessary.
The final stage of osteoarthritis is end-stage osteoarthritis. It causes severe chronic inflammation and irreversible damage to the joints, which leads to permanent loss of physical activity.
SymptomsEnd-stage osteoarthritis deteriorates joints completely and shows severe symptoms which may include.

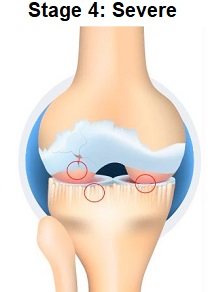
End-stage osteoarthritis causes irreversible damage to the joints, manageable by medications and surgical procedures.
Osteoarthritis can occur in any part of the body. According to National Institute on Aging, osteoarthritis can be seen in the hands, knees, spine, hip, and weight-bearing joints of the body. The 4 stages of osteoarthritis in different body parts are listed below.
What are the 4 stages of osteoarthritis in the hands?
Stage 1: Minor damage of the joint or bone spur formation.
Stage 2: Initiation of pain and stiffness of joints.
Stage 3: Loss of cartilage which leads to friction between two joints.
Stage 4: Severe pain, complete joint damage, and loss of hands movement occur.
Stage 1: Minor cartilage damage. Stage 2: Change in disc space with mild pain and stiffness of spine. Stage 3: Moderate pain along with the spine compression. Stage 4: Severe pain and loss of spine function.
Whatare the 4 stages of osteoarthritis knee?Stage 1: Minor cartilage destruction that causes discomfort. Stage 2: Initiation of ache and tenderness around the knee joint. Stage 3: Significant cartilage loss and decreased knee flexibility. Stage 4: Strong feeling of ache, loss of cartilage, increased joint friction, and loss of knee movement.
What are the 4 stages of osteoarthritis in the shoulder?
This inflammatory form of arthritis causes joint pain, swelling and damage. Learn more about RA and how to treat it.
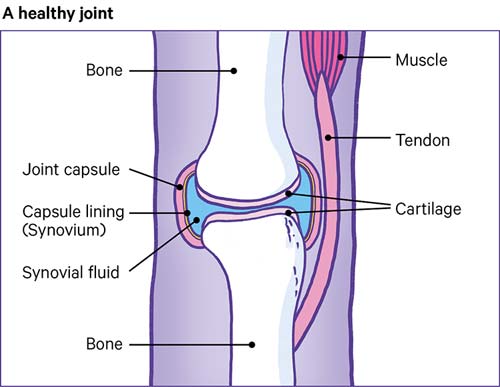
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) causes joint inflammation and pain. It happens when the immune system doesn’t work properly and attacks the lining of the joints, called the synovium. The disease commonly affects the hands, knees or ankles, and usually the same joint on both sides of the body, such as both hands and both knees. But sometimes RA causes problems in other parts of the body as well, such as the eyes, heart and circulatory system and/or the lungs.
For unknown reasons, more women than men get RA, and it usually develops in middle age. Having a family member with RA increases the odds of developing RA.
Causes:In a healthy person, the immune system fights invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. With an autoimmune disease like RA, the immune system mistakes the body’s cells for foreign invaders and releases inflammatory chemicals that attack those cells. Tn RA, it attacks the synovium, the tissue lining around a joint that produces a fluid to help the joint move smoothly. The inflamed synovium gets thicker and makes the joint area feel painful and tender and look red and swollen, and moving the joint may be difficult.
Researchers aren’t sure why people develop RA. They believe these individuals may have certain genes that are activated by a trigger in the environment, such as a virus or bacteria, physical or emotional stress or some other external factor.
Symptoms:In the early stages, people with RA may not see redness or swelling in the joints, but they may experience tenderness and pain. These symptoms are clues to RA:
Many people with RA get very tired (fatigue) and some may have a low-grade fever. RA symptoms may come and go. Having a lot of inflammation and other symptoms is called a flare. A flare can last for days or months.
Health Effects:
Getting an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible is the first step to treating RA effectively. A doctor with specialized training in treating arthritis (called a rheumatologist) is the best person to make a correct diagnosis, using medical history, a physical examination and lab tests.
Medical history. The doctor will ask about joint symptoms (pain, tenderness, stiffness, difficulty moving), when they started, if they come and go, how severe they are, what actions make them better or worse and whether family members have RA or another autoimmune disease.
Physical examination. The doctor will look for joint tenderness, swelling, warmth and painful or limited movement,
bumps under the skin or a low-grade fever.
Blood tests. The blood tests look for inflammation and blood proteins (antibodies) that are linked to RA:
Imaging tests. RA can cause the ends of the bones within a joint to wear down (erosions). An X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan can look for erosions. But if they don’t show up on the first tests that could mean RA is in an early stage and hasn’t damaged bone yet. Imaging results can also show how well treatment is working.
TreatmentThe goals of RA treatment are to:
Working with your doctor to ensure you get appropriate medical treatment is essential, but you can also take measures on your own to manage your RA and ease pain and fatigue. Diet, exercise, smoking cessation and mental health are all key to good health overall and controlling RA.
Healthy Eating. A balanced, nutritious diet consisting of the recommended amounts of all the food groups helps promote wellness and makes it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
Daily movement. Even when you don’t have time to exercise, try to make movement part of your everyday routine. Use the stairs instead of taking the elevator. Park in a spot that makes you walk a bit to enter a building. Take the longer way to a meeting in your office.
Balancing activity with rest. It's important to try to stay physically active even during a flare, but rest is also especially important when RA is active and joints feel painful, swollen or stiff. Rest helps reduce inflammation and fatigue that can come with a flare. Taking breaks throughout the day protects joints and preserves energy.
Hot and cold treatments. Heat treatments, such as heat pads or warm baths, tend to work best for soothing stiff joints and tired muscles. Cold is best for acute pain and swollen joints. It can numb painful areas and reduce inflammation.
Topical products. These creams, gels or stick-on patches can ease the pain in a joint or muscle. Some contain the medicine that you can get in a pill, and others use ingredients that irritate your nerves to distract from pain.
Stress Reduction and Complementary Therapies. There are different ways to relax and stop focusing on pain. They include meditation, deep breathing, and thinking about images in your mind that make you feel happy. Massage can help reduce pain, relax sore muscles and ease stress or anxiety. Acupuncture involves inserting fine needles into the body along special points to relieve pain. If you don’t like needles, acupressure uses firm pressure instead.
Gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis that is very painful. It usually affects one joint at a time (often the big toe joint). There are times when symptoms get worse, known as flares, and times when there are no symptoms, known as remission. Repeated bouts of gout can lead to gouty arthritis, a worsening form of arthritis. There is no cure for gout, but you can effectively treat and manage the condition with medication and self-management strategies.
What are the signs and symptoms of gout?Gout flares start suddenly and can last days or weeks. These flares are followed by long periods of remission—weeks, months, or years—without symptoms before another flare begins. Gout usually occurs in only one joint at a time. It is often found in the big toe. Along with the big toe, joints that are commonly affected are the lesser toe joints, the ankle, and the knee.
Symptoms in the affected joint(s) may include:
Gout is caused by a condition known as hyperuricemia, where there is too much uric acid in the body. The body makes uric acid when it breaks down purines, which are found in your body and the foods you eat. When there is too much uric acid in the body, uric acid crystals (monosodium urate) can build up in joints, fluids, and tissues within the body. Hyperuricemia does not always cause gout, and hyperuricemia without gout symptoms does not need to be treated.
What increases your chances for gout?The following make it more likely that you will develop hyperuricemia, which causes gout:
A medical doctor diagnoses gout by assessing your symptoms and the results of your physical examination, X-rays, and lab tests. Gout can only be diagnosed during a flare when a joint is hot, swollen, and painful and when a lab test finds uric acid crystals in the affected joint.
How is gout treated?Gout can be effectively treated and managed with medical treatment andwho should diagnose and treat gout? The disease should be diagnosed and treated by a doctor or a team of doctors who specialize in care of gout patients. This is important because the signs and symptoms of gout are not specific and can look like signs and symptoms of other inflammatory diseases. Doctors who specialize in gout and other forms of arthritis are called rheumatologists.
Your health care provider may recommend a medical treatment plan to
Gout affects many aspects of daily living, including work and leisure activities. Fortunately, there are many low-cost self-management strategies that are proven to improve the quality of life of people with gout. For gout in particular:
Get physically active. Experts recommend that adults engage in 150 minutes per week of at least moderate physical activity. Every minute of activity counts, and any activity is better than none. Moderate, low impact activities recommended include walking, swimming, or biking. Regular physical activity can also reduce the risk of developing other chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Go to effective physical activity programs. For people who worry that physical activity may make arthritis worse or are unsure how to exercise safely, participation in physical activity programs can help reduce pain and disability related to arthritis and improve mood and the ability to move.Classes take place at local Ys, parks, and community centers.

Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis linked with psoriasis, a chronic skin and nail disease. Psoriasis causes red, scaly rashes and thick, pitted fingernails. Psoriatic arthritis is similar to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in symptoms and joint swelling (inflammation). But it tends to affect fewer joints than RA. And it does not make the typical RA antibodies.
The arthritis of psoriatic arthritis comes in 5 forms:
Doctors don't know what causes psoriatic arthritis. But factors such as immunity, genes, and the environment may play a role.
What are the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis?The psoriasis symptoms may start before or after the arthritis. Psoriasis causes red, scaly rashes and thick, pitted fingernails. About 3 in 20 to 3 in 10 people with psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis. Symptoms of psoriatic arthritis may include:
The symptoms of psoriatic arthritis can look like other health conditions. Make sure to see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is psoriatic arthritis diagnosed?Psoriatic arthritis is easier to confirm if you already have psoriasis. If you don’t have the skin symptoms, diagnosis is more difficult. The process starts with a health history and a physical exam. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms. You may have blood tests to check the following:
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on the severity of your condition.
Both the skin condition and the joint inflammation are treated. Early diagnosis and treatment helps prevent joint damage. Some medicines used to treat psoriatic arthritis include:
The condition may damage joints enough to change your activity level. Lack of activity can lead to stiff joints and muscle weakness. Psoriatic arthritis can also cause tiredness (fatigue) and low red blood cell count (anemia). You are more likely to develop:
There is no cure for psoriatic arthritis. But you can reduce your symptoms by sticking to your treatment plan. Manage pain with medicine, acupuncture, and meditation. Get enough exercise. Good exercises include yoga, swimming, walking, and bicycling. Work with a physical or occupational therapist. He or she can suggest devices to help you with your daily tasks. When should I call my healthcare provider?
Let your healthcare provider know if your symptoms get worse or you have new symptoms.
Key Points about Psoriatic Arthritis
It’s a unique formulation in many means. At first it’s the only natural formulation that can block 6-8 inflammatory mediators. Secondly it is composed of most effective natural ingredients to be studied and proven safe.
In most of cases, mild to moderate symptoms, users usually feel reduction in their symptoms score after 10 days of initiation of Aveoxx Advance.
In addition to this, users with moderately severe stage of disorder, they get relieved from pain, stiffness and muscular rigidity within 1month after initiation of therapy.
Yes, absolutely, it can be given with any class of medication. No side effects reported. But it’s suggested that while talking Aveoxx Advance, no other medication like NSAIDS is taken.
Both the formulation have different mode of actions. Glucosamine and Chondroitin supplements play a supportive role in cartilage health whereas Aveoxx Advance is specially formulated to reduce joint pain, stiffness, muscular rigidity, spasms and swelling in one or more joints.


